Pest Control
Earwig Pest Control Guide: Managing the Common Pincher Bug

Effective Earwig Pest Control Methods
Earwigs, often called “Pincher Bugs,” can invade homes, especially during hot or dry weather. Effective earwig pest control can help manage these insects and keep your home pest-free.
How to Identify Earwigs
Earwigs are dark brown insects with curved pincers at the end of their abdomen. They are usually 1 inch long with long antennae. Despite their intimidating appearance, earwigs are harmless to humans and rarely bite.
Common Types of Earwigs
The European earwig is the most common species in the United States. Other types include the Red-Legged earwig, Striped earwig, and Giant St. Helena earwig. They thrive in cool, damp environments.
Where Earwigs Hide
Earwigs prefer moist, shaded areas outdoors. They often hide under rocks, logs, or piles of leaves. Indoors, they gather in basements, bathrooms, or kitchens where moisture is present.
What Earwigs Eat
Earwigs consume decaying organic matter, plants, and small insects. While they help control mites and aphids, they can damage garden plants if populations grow.
Effective Earwig Pest Control Methods
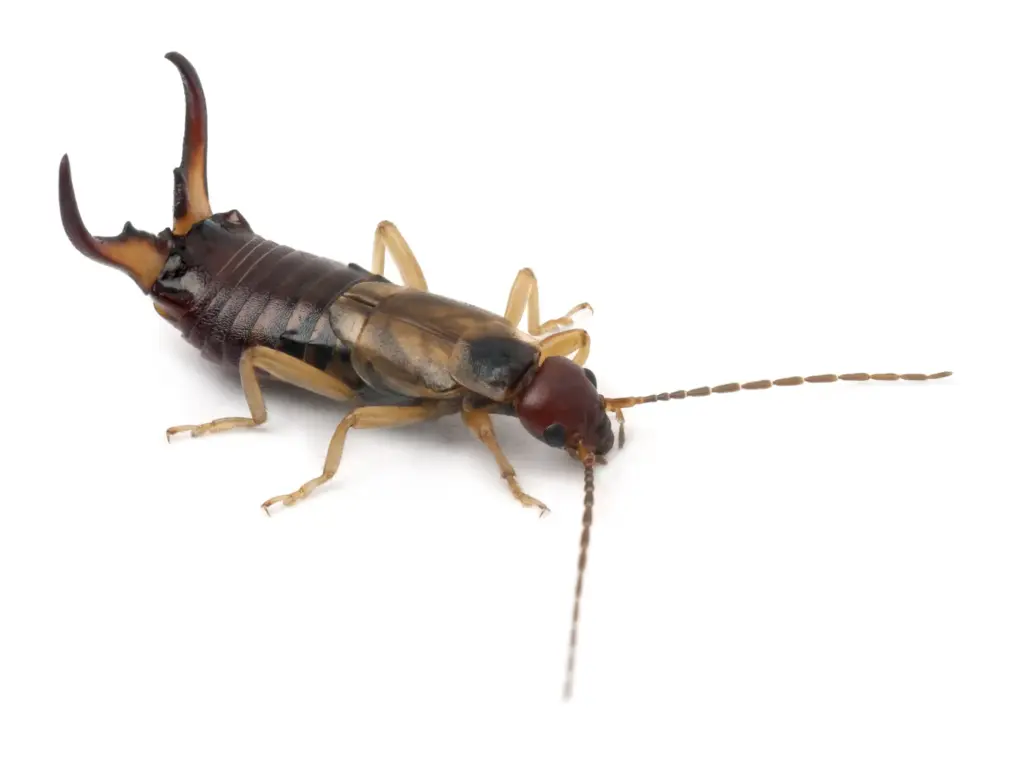

Courtesy of Envato
Signs of Earwigs
Look for earwigs in damp places, under garden debris, or near leaking pipes. Their presence often indicates excessive moisture.
Control Techniques
- Traps: Place a shallow dish with oil or soy sauce to trap and drown earwigs.
- Insecticides: Use alcohol-based sprays for quick indoor control.
- Vacuuming: Removing visible earwigs with a vacuum keeps numbers low.
- Natural Predators: Birds and frogs naturally reduce earwig populations.
Prevention Tips
- Eliminate Hiding Spots: Clear away mulch, logs, and debris near your home.
- Seal Cracks: Close entry points like window gaps and door cracks.
- Reduce Moisture: Fix leaks and ensure gutters drain properly.
Conclusion
With these strategies, you can manage earwigs effectively and maintain a pest-free home. For persistent issues, consult a pest control professional. Explore more home tips and pest control strategies on this website.