Lightning & Electrical
How to Identify the Different Types of Circuit Breakers
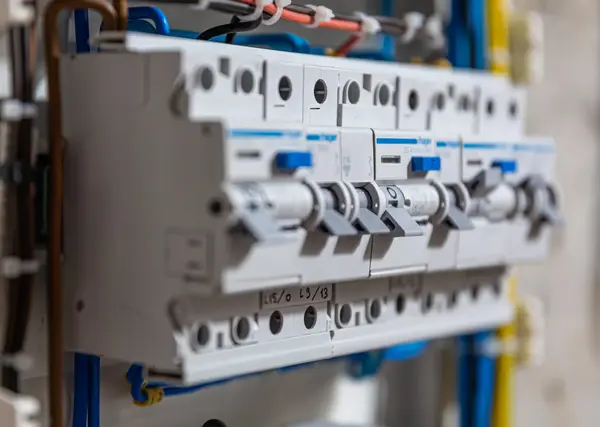

Here’s a breakdown of the 5 types of circuit breakers commonly found in homes:
1. Standard, Single-Pole Circuit Breaker

- Purpose: Protects a single 15-amp or 20-amp circuit, often used for lighting and small appliances.
- Function: The breaker trips when the circuit exceeds its rated current, preventing overheating and electrical fires.
- Common Use: Living room lights, kitchen receptacles, etc.
2. Standard, Double-Pole Circuit Breaker

- Purpose: Used for larger appliances that require more power, such as air conditioners, dryers, and ovens.
- Function: Connects to two hot wires and trips both at the same time to prevent a half-hot circuit.
- Common Use: Large appliances that need 240V (e.g., electric range).
3. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Breaker

- Purpose: Protects against ground faults, which occur when electricity takes an unintended path (like through water or a person).
- Function: Detects discrepancies in the current and shuts off the circuit if the difference is more than 6 milliamps, preventing shocks.
- Common Use: Kitchens, bathrooms, garages, and outdoor outlets where water is a risk.
4. Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) Breaker

- Purpose: Protects against electrical arcs caused by faulty wiring or loose connections that could lead to fires.
- Function: Detects unintentional electrical arcs and cuts the power to prevent a fire hazard.
- Common Use: Bedrooms, living rooms, and other areas where wiring faults could go unnoticed.
5. AFCI/GFCI Dual-Function Breaker

- Purpose: Combines both AFCI and GFCI protection, ideal for areas like kitchens and laundry rooms.
- Function: Offers both arc fault and ground fault protection in a single breaker, which saves space in your panel.
- Common Use: Modern homes or remodeled kitchens and laundry areas.
Each type of breaker serves a distinct safety purpose, and knowing when and where to use each type helps prevent electrical hazards in your home.
Continue Reading